Pregnancy-related deaths are a critical public health concern, particularly in the United States, where these fatalities continue to rise alarmingly. More than 80 percent of these deaths are deemed preventable, yet the U.S. maintains the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income nations. A recent study highlights significant disparities in pregnancy-related deaths based on state, race, and ethnicity, revealing a dire need for better prenatal and postpartum care. Factors such as health disparities and the COVID-19 pandemic’s impact are contributing to this troubling trend. To address this crisis effectively, a comprehensive understanding of maternal health and persistent inequities is not just necessary but urgent.
The alarming rise in fatalities associated with pregnancy underscores the pressing issue of maternal health in the U.S., where these tragic occurrences remain unacceptably high. Known as maternal mortality, these deaths can often be linked to inadequacies in both prenatal and postpartum support systems, emphasizing the necessity for enhanced healthcare measures. The increase in pregnancy-associated deaths—particularly in marginalized communities—reflects broader health disparities that have been exacerbated by events like the COVID-19 outbreak. Therefore, it’s crucial for healthcare policies to focus on rectifying these imbalances and ensuring that every individual has equitable access to quality maternity and postpartum care. A renewed commitment to understanding and addressing these issues is vital for safeguarding maternal health.
Understanding the Rise in U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths
The United States is facing an alarming increase in pregnancy-related deaths, with a rate that consistently outpaces other high-income countries. Experts attribute this troubling trend to a complex interplay of factors, including healthcare access disparities, systemic biases, and chronic health conditions that many expectant mothers face. A recent study highlighted that more than 80% of these deaths are preventable, emphasizing a pressing need for enhanced prenatal and postpartum care to address the gaps in the current system.
Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated the situation, leading to significant spikes in pregnancy-related deaths, especially in 2021. State-level disparities in maternal mortality rates further complicate the issue, revealing that certain demographics, particularly American Indian and Alaska Native women, experience mortality rates nearly four times higher than their white counterparts. Addressing these disparities requires urgent policy reform and a dedicated effort to improve healthcare infrastructure across all states.
The Impact of Health Disparities on Maternal Mortality
Health disparities play a critical role in the rising rates of maternal mortality in the U.S. Racial and ethnic minorities, particularly non-Hispanic Black and American Indian women, face higher risks of pregnancy-related death due to a combination of factors, including inadequate access to quality healthcare, socioeconomic challenges, and underlying health conditions. The findings reveal a systemic issue where societal inequities directly influence health outcomes, leading to preventable deaths during and after pregnancy.
Efforts to combat these disparities have been limited, with only partial policy implementations showing promise. Innovative initiatives aimed at closing the racial gap in maternal health are essential to effect positive change. By prioritizing equitable healthcare access, addressing prenatal care barriers, and focusing on postpartum care, the U.S. can begin to dismantle the systemic issues contributing to the alarming rise in pregnancy-related deaths.
The Role of Prenatal and Postpartum Care in Maternal Health
Prenatal and postpartum care are crucial components of maternal health, impacting the well-being of both mothers and infants. Comprehensive prenatal care can identify potential complications early, provide necessary treatments, and empower women with knowledge about their health and that of their babies. Despite its importance, many women in the U.S. lack access to consistent and quality prenatal services, contributing to higher risks of maternal mortality.
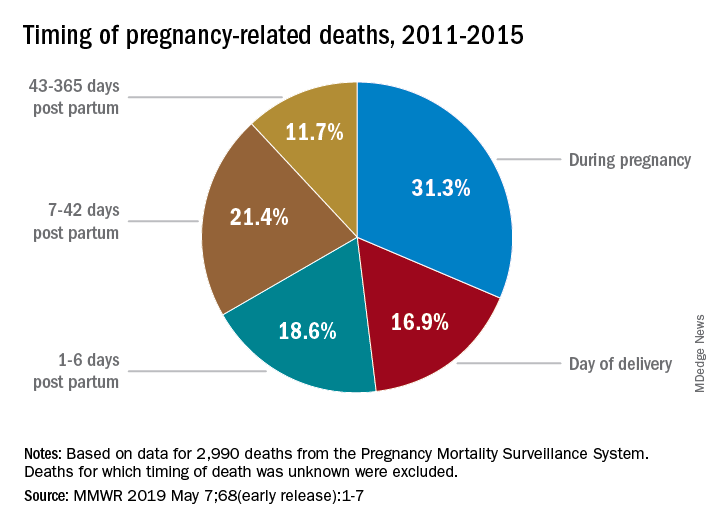
Postpartum care is equally vital, yet it often receives insufficient attention, especially beyond the initial six-week check-up. The recognition that maternal health extends into the first year after childbirth underscores the importance of continuous support and medical follow-up. Improving postpartum services can significantly reduce late maternal deaths, a category often overlooked in traditional maternal mortality statistics, thereby enhancing overall maternal health outcomes.
The Impact of COVID-19 on Maternal Mortality Rates
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a devastating impact on various aspects of public health, and maternal health is no exception. Initial data showed a sharp increase in pregnancy-related deaths during the pandemic, particularly as healthcare systems became overwhelmed and access to routine care diminished. As pregnant individuals faced heightened risks from the virus, the pandemic exacerbated pre-existing health disparities and barriers to care, further contributing to elevated maternal mortality rates.
As the nation continues to navigate the aftereffects of the pandemic, it is crucial to assess how COVID-19 has reshaped prenatal and postpartum care landscapes. Implementing proactive measures, including improved telehealth services and adjusted care protocols, can help mitigate the long-term consequences of the pandemic on maternal health. Addressing these challenges head-on with innovative strategies is essential to improving outcomes and saving lives.
Addressing Systemic Bias in Maternal Healthcare
Systemic bias within the healthcare system greatly impacts maternal health outcomes, particularly for women of color and marginalized communities. Implicit biases can lead to disparities in diagnosis, treatment accessibility, and quality of care received, contributing to the troubling rise in pregnancy-related deaths. To combat these biases, healthcare providers must undergo training to recognize and address their prejudices while promoting an inclusive environment for all patients.
In addition, community engagement and advocacy are vital to developing a culturally competent healthcare workforce that understands and respects the diverse needs of pregnant women. By focusing on equitable treatment and personalized care, healthcare systems can significantly contribute to reducing maternal mortality rates, ultimately creating a safer and more supportive environment for expectant mothers.
Preventing Pregnancy-Related Deaths Through Policy Reform
Policy reform is essential to address the increasing rates of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. A comprehensive approach would involve revisiting current maternal health policies to ensure they prioritize preventive care, equitable access, and comprehensive support systems for pregnant individuals. Lawmakers must prioritize funding for maternal health programs that aim to reduce disparities and improve care quality across states.
Investing in innovative solutions and research initiatives will be vital to identifying effective strategies for enhancing maternal health outcomes. By learning from successful models, such as those implemented in states with lower maternal mortality rates, the U.S. can create a framework for improving care across all demographics. Ensuring sustained funding and commitment to maternal health is paramount to reversing the troubling trend of rising pregnancy-related deaths.
The Importance of Education and Awareness in Maternal Health
Raising awareness about maternal health issues is critical for fostering a supportive environment for pregnant women. Education plays a significant role in equipping individuals with knowledge about available resources, potential risks, and healthy practices during pregnancy and postpartum. By integrating maternal health education into community programs, healthcare providers can empower women to advocate for their health and the health of their babies.
Additionally, public health campaigns aimed at informing individuals about the warning signs and risk factors associated with pregnancy-related complications can lead to timely interventions. Heightened awareness can encourage more women to seek care when necessary, significantly reducing the risk of preventable pregnancy-related deaths. A well-informed community can drive demand for improved healthcare services and accountability from healthcare providers.
Innovative Solutions to Enhance Prenatal Care Access
Addressing the barriers to accessing prenatal care is crucial for reducing maternal mortality. Innovative solutions such as mobile health clinics, telehealth services, and community outreach programs can bridge gaps in service delivery, particularly for underserved populations. These initiatives can ensure that expectant mothers receive timely and adequate prenatal care, regardless of their geographical location or socioeconomic status.
Healthcare systems must also prioritize integrating mental health services into prenatal care to address the holistic needs of pregnant women. Recognizing the connection between mental and physical health can lead to more effective interventions, ultimately supporting healthier pregnancies and reducing maternal health risks. By adopting these innovative approaches, we can enhance access to quality maternal healthcare and significantly improve outcomes.
Long-Term Care Considerations for Maternal Health
Long-term care for maternal health encompasses not just the period of pregnancy but extends into the postpartum year and beyond. As outlined in recent studies, repeatedly overlooking this critical time frame contributes to the rising rates of late maternal deaths. It is imperative that healthcare systems evolve to include comprehensive strategies that address women’s health as a continuum, ensuring that mothers receive the ongoing care they need after childbirth.
Enhancing long-term care can significantly affect women’s health outcomes, enabling timely interventions for chronic conditions that may arise during or after pregnancy. By facilitating better communication and establishing follow-up protocols, healthcare providers can effectively monitor patients and address concerns that emerge in the postpartum period. This focused attention on maternal health beyond the initial months after delivery is key to reducing mortality rates and improving overall well-being.
The Future of Maternal Health: Collaborative Efforts for Change
The future of maternal health in the U.S. relies heavily on collaborative efforts between policymakers, healthcare providers, and the community. Addressing the multifaceted challenges of maternal mortality requires a united front where stakeholders actively engage in promoting equitable access to quality care. By advocating for policies that prioritize women’s health and investing in maternal health infrastructure, we can pave the way for meaningful improvements.
Future initiatives must also emphasize the importance of community engagement, focusing on culturally competent care and support systems that cater to diverse populations. By fostering partnerships between healthcare systems and community organizations, we can ensure that every expecting mother has access to the resources and education she needs. Together, we can work towards a future where pregnancy-related deaths are minimized, and all mothers receive the compassionate care they deserve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
The leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. include cardiovascular disease, hemorrhage, and complications from chronic medical conditions. Recent data indicate that over 20% of these deaths are due to cardiovascular issues, such as hypertension and cardiac arrest, highlighting the need for improved prenatal care and management of chronic conditions in pregnant individuals.
How does the U.S. maternal mortality rate compare to other high-income countries?
The U.S. continues to lead among high-income countries in maternal mortality rates, with significant disparities based on state, race, and ethnicity. Factors contributing to this include inequitable health policies, access to quality care, and systemic biases within the healthcare system.
What role does prenatal care play in preventing pregnancy-related deaths?
Quality prenatal care is crucial in identifying and managing health issues before, during, and after pregnancy. Approximately 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable with adequate prenatal and postpartum care, emphasizing the need for comprehensive healthcare services that address potential complications early.
How has COVID-19 impacted pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on pregnancy-related deaths, particularly in 2021, as many individuals faced disruptions in care and increased health risks. This led to a rise in the maternal mortality rate as pregnant individuals were more susceptible to complications, indicating a need for improved health system responses during public health emergencies.
Why are health disparities significant in the context of pregnancy-related deaths?
Health disparities significantly affect pregnancy-related deaths, as certain racial and ethnic groups experience higher mortality rates. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women have rates nearly four times higher than white women. Addressing these disparities requires targeted policies and healthcare practices that ensure equitable access to quality maternal care across all demographic groups.
What are late maternal deaths and why are they important?
Late maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year after pregnancy. They are significant because they highlight gaps in postpartum care and the ongoing health needs of new mothers. Recognizing this timeframe is essential for developing better healthcare systems that continue to support women’s health beyond the initial postpartum period.
What steps can be taken to improve maternal health outcomes in the U.S.?
Improving maternal health outcomes requires sustained investment in public health infrastructure to enhance both prenatal and postpartum care. States need to address policy disparities influencing maternal death rates, alongside advocating for innovative solutions to ensure comprehensive care throughout pregnancy and the postpartum period.
How can policymakers address the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths?
Policymakers can address rising pregnancy-related deaths by investing in expanded access to prenatal and postpartum care, particularly in underserved areas. They should also work to eliminate systemic biases in healthcare, promote equitable care policies, and ensure that maternal health remains a priority in public health funding and research.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Increasing Rates | Pregnancy-related deaths are on the rise in the U.S., reaching 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2022. |
| Preventable Deaths | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, indicating a critical need for improved healthcare access and practices. |
| Disparities by Race and Ethnicity | American Indian and Alaska Native women face a mortality rate nearly four times that of white women, showcasing significant racial health disparities. |
| Leading Causes | Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death among pregnant women, accounting for over 20% of cases. |
| Importance of Extended Postpartum Care | Late maternal deaths, occurring between 42 days and 1 year postpartum, account for nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths, emphasizing the need for ongoing care. |
| Need for Systemic Change | The U.S. healthcare system requires policies that address inequities and enhance the quality of maternal care, particularly during and after pregnancy. |
Summary
Pregnancy-related deaths have been a pressing issue in the United States, where alarming rates continue to rise despite being largely preventable. The findings suggest that with over 80% of these deaths classified as preventable, there is a dire need for enhanced prenatal care, systemic reforms, and comprehensive postpartum support. By implementing effective policies and focusing on reducing disparities among racial and ethnic groups, it is possible to significantly improve maternal health outcomes in the U.S.