Alzheimer’s disease research is at the forefront of tackling one of the most pressing neurodegenerative diseases affecting millions globally. Pioneering scientists like Beth Stevens are reshaping our understanding of microglial cells, which play a crucial role in the brain’s immune system by clearing out toxins and ensuring healthy neural connections. Recent studies show that dysfunctional pruning of synapses by microglia can contribute to the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, emphasizing the importance of this area of study in developing Alzheimer’s treatment. As Stevens’ lab at Boston Children’s Hospital and the Broad Institute demonstrates, uncovering the mechanisms behind these immune responses can lead to identifying potential biomarkers and therapeutic strategies that hold promise for early intervention. With the number of Alzheimer’s patients expected to rise dramatically, the insights gained from this ongoing research are critical to changing the trajectory of care and improving quality of life for those battle this relentless disease.
In the realm of cognitive decline, studies focusing on memory loss disorders have gained immense traction, especially as scientists delve deeper into cellular processes governing brain health. The exploration of immune-like cells in the central nervous system, such as microglia, reveals their dual role in maintaining overall neural function and their potential negative impact in diseases like dementia. By addressing the underlying mechanisms of neuroinflammation and synaptic pruning, researchers are unveiling novel avenues for intervention. With the invaluable work of leading researchers like Stevens, this critical research serves as the backbone for future advancements in treatments aimed at combating various forms of dementia and enhancing the lives of affected individuals.
The Role of Microglial Cells in Alzheimer’s Research
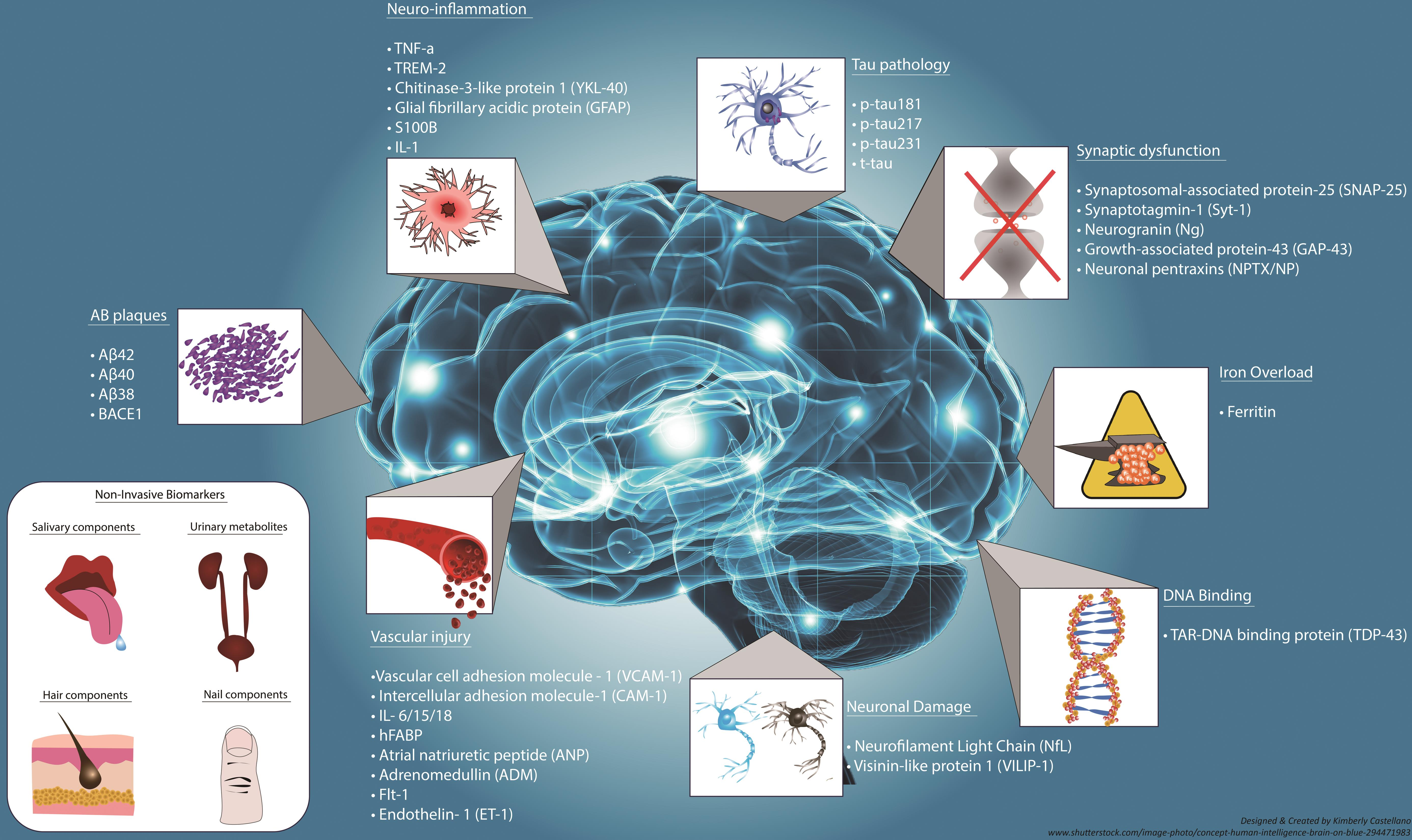
Microglial cells play a crucial role in the brain’s immune system, acting as the first line of defense against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. These specialized cells constantly survey the brain, identifying and removing damaged neurons and other debris that can contribute to disease progression. Recent research has demonstrated that improper functioning of microglia can lead to excessive synaptic pruning, a phenomenon that may play a key role in the onset of Alzheimer’s disease. Understanding the precise functions of microglial cells is essential for developing new treatment strategies that could potentially halt or reverse the damage caused by these devastating conditions.
Beth Stevens’ pioneering work has significantly altered our understanding of microglial roles, moving beyond traditional views that saw them solely as cleanup agents. Her lab’s discoveries have suggested that the neuroinflammatory processes mediated by these cells can either promote health or contribute to neurodegeneration, depending on their activation states. This duality highlights the importance of targeting microglial function in Alzheimer’s treatment, as interventions that can modulate their activity may improve patient outcomes and slow disease progression.
Innovative Approaches to Alzheimer’s Treatment
The landscape of Alzheimer’s treatment is rapidly evolving, with innovative research focusing on molecular and cellular pathways influenced by microglial activity. By investigating how these immune cells interact with synapses in healthy and diseased states, scientists like Beth Stevens are opening doors to novel therapeutic avenues. The identification of specific biomarkers linked to abnormal microglial function could lead to earlier diagnosis and tailored treatment plans, significantly enhancing the effectiveness of Alzheimer’s therapies.
Moreover, the development of drugs targeting the pathways associated with microglial behavior may revolutionize Alzheimer’s treatment. As research progresses, therapies that aim to restore the natural balance of microglial cells could mitigate their destructive pruning activity while maintaining their beneficial functions. Such targeted therapies not only hold promise for Alzheimer’s but could also have implications for other neurodegenerative diseases, demonstrating the interconnectedness of brain health and immune system activity.
Understanding Neuroinflammation and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neuroinflammation is increasingly recognized as a critical component in the progression of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s. The brain’s immune response is mediated largely by microglial cells, which can become hyperactive in the presence of neurodegeneration. This heightened state of inflammation can exacerbate cognitive decline and neurodegeneration, creating a vicious cycle that complicates treatment. Current research aims to unravel the complex interactions between neuroinflammation and neuronal health, paving the way toward more effective therapies.
By deepening our understanding of how neuroinflammatory pathways interact with neurodegeneration, researchers are discovering potential targets for interventions. For instance, modifying the behavior of microglial cells could reduce inflammation while enhancing their protective roles. The link between neuroinflammation and synaptic dysfunction is a promising avenue for investigations aiming to mitigate the effects of Alzheimer’s and similar disorders, thus providing hope for millions affected by these conditions.
Beth Stevens: A Leader in Alzheimer’s Disease Research
Dr. Beth Stevens has emerged as a leading figure in Alzheimer’s disease research, drawing attention to the vital role that microglial cells play in brain health. Her groundbreaking findings challenge conventional wisdom about the brain’s immune system, revealing how microglia’s actions, whether beneficial or harmful, have far-reaching implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Stevens’ approach combines meticulous basic science with a keen sense of curiosity, exemplifying how fundamental research can lead to meaningful advancements in understanding complex diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Her achievements have not gone unnoticed, earning her prestigious accolades such as the MacArthur Fellowship, which recognizes individuals who have shown exceptional originality and dedication in their professional fields. Through her work, Stevens inspires a new generation of scientists to consider the underlying mechanisms of Alzheimer’s disease, emphasizing that understanding the biological processes at play is essential for developing effective treatment options for the estimated 7 million Americans living with this debilitating condition.
The Future of Alzheimer’s Research: Challenges and Opportunities
The future of Alzheimer’s research is filled with both challenges and opportunities, especially as the population ages and the prevalence of the disease continues to rise. As scientists strive to better understand the pathological mechanisms behind Alzheimer’s, there is an urgent need for collaboration across disciplines. Innovations in molecular biology, neuroimaging, and bioinformatics can provide greater insights into the interplay between microglial function and neurodegeneration, creating a multifaceted approach to unravel the complexities of Alzheimer’s.
Furthermore, the integration of patient data with laboratory findings can help distill clinically relevant insights that guide therapeutic development. As researchers like Beth Stevens advance our understanding of microglial involvement in Alzheimer’s, the potential to develop targeted therapies grows, offering hope for improved patient outcomes. Addressing the challenges of funding, resource allocation, and interdisciplinary communication will be crucial for translating breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s research into tangible treatments.
The Importance of Early Detection in Alzheimer’s Disease
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease is critical to managing its progression and improving quality of life for patients. With the potential for biomarkers linked to microglial activity, researchers are paving the way for diagnostic tests that could identify Alzheimer’s in its nascent stages. Identifying neuroinflammation or aberrant synaptic pruning before significant cognitive impairment occurs can greatly affect treatment outcomes and delay disease onset.
The advancements in understanding the role of microglial cells have opened possibilities for developing screening tools that assess brain health. As research continues to evolve, integrating these biomarkers into clinical practice could facilitate earlier intervention strategies and personalized treatments for patients at risk. The connection between early detection and successful Alzheimer’s treatment is paramount in the fight against this debilitating disease.
Collaboration in Alzheimer’s Disease Research: A Collective Effort
Collaboration among researchers, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies is essential to address the complexities of Alzheimer’s disease. The challenges of understanding this multifaceted disorder require diverse expertise and interdisciplinary approaches. By combining insights from neurobiology, immunology, and clinical science, teams can comprehensively analyze how conditions like aberrant microglial activity contribute to Alzheimer’s.
Beth Stevens represents a model for collaborative research, continuously engaging with other scientists and institutions to further Alzheimer’s understanding. Such collaboration can harness collective knowledge and resources, promoting innovative solutions that cater to the diverse needs of Alzheimer’s patients. This unified approach fosters an ecosystem where research can thrive, translating into clinically relevant strategies that eventually lead to effective treatments.
Impacts of Aging on Alzheimer’s Disease Progression
Aging is the greatest risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease, influencing both the pathology and clinical manifestations of the disorder. As individuals age, the functions of microglial cells can alter significantly, leading to impaired immune responses within the brain. This decline in microglial health raises the risk of neuroinflammation and synaptic dysfunction, contributing to the progression of Alzheimer’s disease and similar neurodegenerative conditions.
Research into the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which aging affects microglial function is crucial for developing intervention strategies. Understanding how these cells change with age allows scientists to identify target points for therapies that could support brain health in aging populations. By addressing the dynamics of aging in Alzheimer’s research, we could improve not only understanding but also treatment and prevention of this widespread disease.
The Economic Burden of Alzheimer’s Disease
The economic burden of Alzheimer’s disease is staggering, with costs projected to soar into the trillions as the population ages. Current estimates suggest that caring for Americans with Alzheimer’s could potentially rise from $360 billion to $1 trillion by 2050. This dramatic increase underscores the urgent need for effective treatments that can alter the course of the disease and significantly lessen its economic impact.
Addressing the costs associated with Alzheimer’s requires innovative research and a robust public health strategy. By investing in studies like those conducted by Beth Stevens, which examine the role of microglia in Alzheimer’s disease, stakeholders can identify opportunities to mitigate economic strain. Preventing or delaying the onset of Alzheimer’s through targeted therapies can reduce healthcare costs and improve patient quality of life, showing that investment in research is essential for both societal and economic reasons.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role do microglial cells play in Alzheimer’s disease research?
Microglial cells are crucial in Alzheimer’s disease research as they act as the brain’s immune system. They help clear out dead or damaged cells and play a significant role in pruning synapses. However, in Alzheimer’s, aberrant pruning by microglia can contribute to neurodegenerative processes. Understanding their function is key to developing effective Alzheimer’s treatments.
How are Beth Stevens’ findings impacting Alzheimer’s treatment?
Beth Stevens’ research has transformed our understanding of microglial cells in the context of Alzheimer’s treatment. Her studies revealed how abnormal microglial activity can lead to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. This has paved the way for pharmaceutical innovations aimed at targeting these immune cells to prevent or mitigate the disease.
Why is research on neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s vital?
Research on neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s is vital due to the increasing number of affected individuals, projected to double in cases by 2050. Understanding the underlying mechanisms, including the role of microglial cells, is essential for creating biomarkers and effective treatments that can alleviate the burden of Alzheimer’s on patients and healthcare systems.
What discoveries have been made about the brain’s immune system in Alzheimer’s disease research?
Recent Alzheimer’s disease research has highlighted the brain’s immune system, particularly the role of microglial cells, in maintaining neural health. Discoveries by researchers like Beth Stevens show how these cells can both protect and potentially harm the brain, revealing new pathways for Alzheimer’s treatment and intervention.
How can understanding synapse pruning help in Alzheimer’s disease research?
Understanding synapse pruning is crucial in Alzheimer’s disease research as it reveals how microglial cells contribute to neuronal health and food debris clearance. Aberrant pruning linked to Alzheimer’s can lead to cognitive decline, making it a critical focus for developing accurate biomarkers and innovative treatments.
What is the significance of Beth Stevens’ work on microglial cells for future Alzheimer’s treatment?
Beth Stevens’ work on microglial cells is significant for future Alzheimer’s treatment as it sheds light on the immune mechanisms involved in neurodegeneration. By identifying how these cells malfunction in Alzheimer’s, her research could lead to targeted therapies that modulate microglial function and improve patient outcomes.
How does federal funding influence Alzheimer’s disease research?
Federal funding is crucial for Alzheimer’s disease research as it supports foundational studies that push the boundaries of our understanding of neurodegenerative diseases. Researchers like Beth Stevens rely on grants from the National Institutes of Health to explore innovative concepts, such as the role of microglial cells in Alzheimer’s.
What potential does microglial research hold for developing Alzheimer’s biomarkers?
Microglial research holds great potential for developing Alzheimer’s biomarkers by uncovering molecular changes associated with abnormal microglial activity. Identifying these biomarkers can lead to earlier detection of the disease, allowing for timely interventions and improved patient management.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Microglial Cells | Act as the brain’s immune system, clear out damaged cells, and prune synapses. |
| Aberrant Pruning | Faulty pruning behavior linked to Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Foundational Research | Research driven by basic science leads to discoveries that impact treatment. |
| Funding Support | Vital federal support through NIH funding enables research progress. |
| Impact on Treatment | Potential to affect treatment for 7 million Americans with Alzheimer’s. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s disease research has made significant strides thanks to innovative studies exploring the role of microglial cells in the brain. By understanding how these immune cells interact with neural networks, researchers like Beth Stevens are unlocking new pathways to detect and treat Alzheimer’s disease. With projections indicating a doubling of Alzheimer’s cases by 2050, continued investment in foundational research is essential to combat this growing health crisis. It’s through curiosity-driven science that we can hope to develop effective therapies and improve the quality of life for millions affected by Alzheimer’s.